ORIENTAL MEDICINE
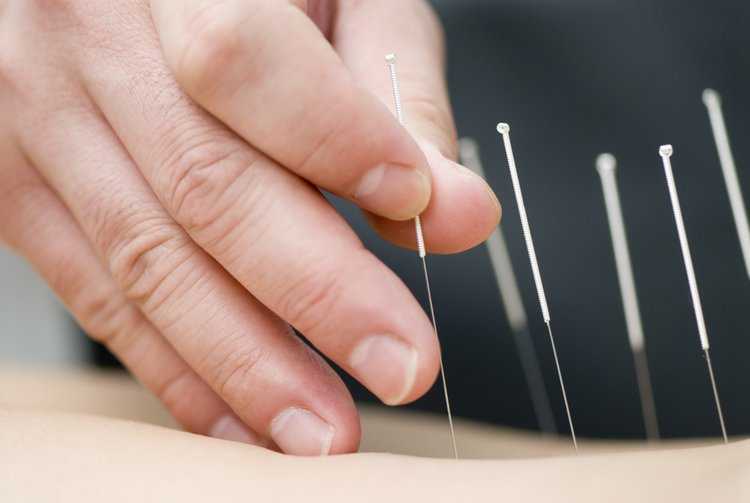
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is the treatment modality of Traditional Chinese Medicine most widely used, recognized and taught in the Western world.
Dating back as far as the Shang Dynasty (1600B.C.), acupuncture involves the gentle insertion of very fine needles at specific points on the body to restore proper functioning of the nervous, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, musculoskeletal and endocrine systems. Acupuncture helps to treat and prevent illness by improving the overall functioning of the body’s immune system.
It presupposes the existence of a vital energy, or "Qi", that is essential to life and that flows throughout the body.
This energy is transported by a system of channels called “Meridians” that represent a large network of superficial and deep pathways that enable a connection between the inner and outer aspects of our bodies.
Acupuncture is a unique therapeutic method that enables us to influence and treat the interior by using a synergy of points on the exterior aspect of our bodies. The healing effect of acupuncture is extensive, and may be used as préventive, alternative and complementary care.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH), and the World Health Organization (WHO) acknowledge Acupuncture to be an effective treatment for a wide variety of common conditions.
Herbal Medicine
TCM herbal medicine is comprised of natural products, mainly of plants and minerals but sometimes of animal origin.
The most frequently used remedies are plant based. Chinese herbal medicine are formula based rather than solely symptom based. Formulas based can be adapted to the patient's body type and treat symdromes or patterns of symptoms.
Chinese herbs are prescribed to address a specific diagnosis. Each herbal formula created is tailored according to specific needs. And because they can be tailored specifically to your symptoms and constitution, formulas allow for various symptoms to be treated at once. Chinese herbs are often used in conjunction with acupuncture to more efficaciously treat a problem or an illness.
One of the reasons Chinese Medicine practitioners in the U.S. prescribe herbs, is to supplement acupuncture treatments between visits since patients can rarely come daily for Acupuncture. Also because certain conditions cannot be treated with Acupuncture alone. Chinese Herbal Formulas, represent the Internal part of Chinese medicine, along with Nutrition which is often used as part of the healing process.
The other advantage of herbs is that they can help re-balance a patient whose physical condition is considered "weak", which is not always possible with Acupuncture alone.
Cupping
Cupping is one of the oldest modalities of traditional Chinese medicine.
It involves placing glass, bamboo, or plastic cups on the skin and creating a vacuum by suctioning out the air. The underlying tissue is raised, or sucked, into the cup. The purpose of cupping is to enhance circulation, help relieve pain, and pull out the toxins that linger in your body's tissues.
During cupping, you are likely to feel a slight sensation of tightness in the area of the cup. Depending on your condition, the cups may be moved around or left in place for 5-10 mns. Cupping causes the skin to temporarily turn red, blue or purple, especially if there is an injury or energetic blockage under the area that was cupped. The skin discoloration can last anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks, but is rarely painful.
Cupping can be helpful in the treatment of stress, pain, allergies, fatigue, flu, colds, back pain, anxiety, and muscle aches. Cupping can also help remove toxins from the body and stimulate the flow of fresh blood, and Qi to the affected area and throughout the body.
Moxibustion
Moxibustion is a form of heat therapy in which dried plant materials called "moxa" are burned on or very near the surface of the skin. The intention is to warm and invigorate the flow of Qi in the body and dispel certain pathogenic influences.
Moxa is usually made from the dried leafy material of Chinese mugwort (Artemesia argyi or A.vlugaris).
Pain due to injury or arthritis, especially in "cold" patterns where the pain naturally feels better with the application of heat.
Moxa is also frequently used for digestive problems and irregular elimination, as well as in gynecological and obstetrical conditions, including the presentation of the breech baby during pregnancy.
Moxibustion can also be used preventively against colds and flu.
Practitioners often deal with both acupuncture and moxibustion during the same clinical session, depending on the diagnosis and treatment strategy.
Gua Sha
Guasha is one of the modalities of traditional Chinese medicine which consists of rubbing with a smooth edge instrument the surface of the skin where resides a subcutaneous lesion or imbalance. When the treatment is effective, a characteristic skin flushing, known as sha, can be observed. This is a favorable response, which provides immediate and lasting benefit of chasing the wind, reducing heat and inflammation, eliminating cold and relieving pain, whether superficial or deep. Guasha is used to treat many acute and chronic health problems, as varied as colds, flu, fever, headache, indigestion, dizziness, injury, joint pain, fibromyalgia and "heat stroke." It is also commonly used to relieve muscular tension and pain, relieve fatigue and weariness.
It is important not to take a shower or bath during the hour following treatment. Shower or bath in cold water should be avoided for at least 24 hours after treatment.
It is also important to keep all areas treated well covered and warm. The area must also be protected from wind exposure, including fans and air conditioning.
Auriculotherapy
The term auriculotherapy often refers to electrical stimulation of the surface of ear reflex points. Specific points on the ear can also be stimulated by manual pressure, referred to as auricular acupressure or ear reflexology. Acupuncture points on the ear can also be stimulated with lasers, magnets, and ear pellets
Auriculotherapy applies the principles of acupuncture to specific points on the ear. It is a treatment modality where the specific malfunctioning organ or a systemic illness can be treated by application of a laser and/or TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) unit to a correlating part of the external ear.
Perfect for patients who do not want to be needled or for children.
Tuina
Tuina is a form of bodywork, it is one of the five branches of Traditional Chinese Medicine that has been used in China for centuries. A combination of massage, acupressure and other forms of body manipulation, tuina works by applying pressure to acupoints, meridians and groups of muscles to remove blockages that prevent the free flow of qi. Removing these blockages restores the balance of qi in the body, leading to improved health and vitality.
Tuina is best suited for rectifying chronic pain, musculoskeletal conditions and stress-related disorders that affect the digestive and/or respiratory systems. Among the conditions tuina treats best are neck pain, shoulder pain, back pain, sciatica and tennis elbow. However, because tuina is designed to improve and restore the flow of qi, treatment often ends up causing improvements to the whole body, not just a specific area.
Commonly used techniques include soft tissue massage; acupressure and manipulation. Practitioners may sometimes use herbal compresses, liniments, ointments and heat to enhance these techniques.